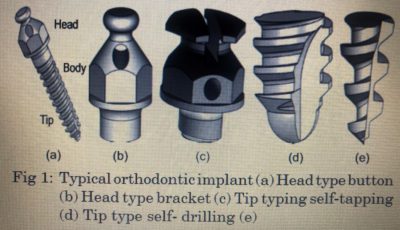
Uses in Dental Practice
Clindamycin as many antibiotics are prescribed in dental practice for either prophylactic or therapeutic use.
Patients allergic to penicillin are treated with clindamycin 300 mg (65%), which is the drug of choice, azithromycin (15%) or metronidazole‐spiramycin combination (13%). Some authors have proposed clindamycin as the drug of choice in view of its good absorption, low incidence of bacterial resistance and the high antibiotic concentrations reached in bone.The antibiotics useful for treating patients with odontogenic infections, according to a study published by the International Dental Journal in 2014.
The oral daily recommended dose is between (150-450 mg) every 6h for at least 7 days, maximum (1.8 g/day) for adults.
IV: (600-900 mg/day) every 8h, maximum dose (4.8 g/day)
Children recommended dose 150 mg every 6 hours for at least 7 days.
Solution dosage form is no longer available in the Jordanian market due to the deficit rate of profit achievement and matching marketing plan goals.
Mechanism of Action
Clindamycin is a semisynthetic Lincoosamide antibiotic, works as bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal at higher concentrations; It binds to 23S RNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit inhibiting protein synthesis.
Available dosage forms in the Jordainian market
– Capsule (150, 300) mg
– IV Injection (300,600) mg
Spectrum of activity
Clindamycin is either bacteriostatic or bactericidal with broad spectrum activity that covers gram positive bacteria such as streptococcus, staphylococcus and pneumococci, most obligate anaerobes especially fragilis. It also carries some activity against Chlamydia trachomatis and protozoans.
Pharmacokinetics
- It penetrates into skeletal muscles as well as soft tissues to treat infections, abscess, sinusitis, bone and joint infections.
- It is highly bounded to serum protein (>90%), metabolized by liver and excreted by urine and bile.
- It has approximately 3 hours half-life.
- No data has been reported for crossing the Blood brain barrier.
- Pregnancy Category B
Common side effects
Rushes, Urticaria, abdominal pain, diarrhea, pseudomembranous enterocollitis, suprainfections, esophagitis, nausea and thrombocytopenia.
Drug interactions
It is reported that Clindamycin have neuromuscular blocking properties that enhance the action of neuromuscular blocking agents. Therefore, it should be used in caution in patients receiving such agents. Clindamycin should not be administered in combination with erythromycin.